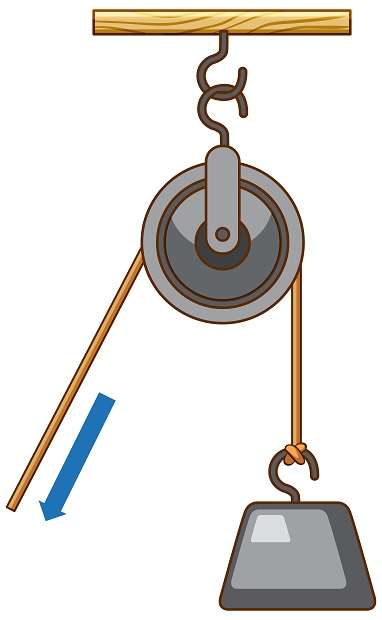
Pulleys – Types and Applications are simple machines that have been used for thousands of years to help lift heavy objects. They consist of a grooved wheel and a rope or cable that passes over it, allowing the user to change the direction of the force required lifting the object. Pulleys have several Types and Applications in daily life and the human system. Pulleys come in different styles and designs, but they all have the same basic principle of operation. When force is applied to one end of the rope, the pulley rotates, transmitting force to the other. Depending on the design of the pulley system, the power can be amplified, reduced, or redirected.
In the human body, there are anatomic Pulleys formed by tendons and retinacula that help to maintain the proper alignment of tendons and reduce friction as they move. These anatomic Pulleys play an essential role in the appropriate functioning of the musculoskeletal system, allowing for efficient movement and reducing wear and tear on the muscles and joints. There are two main Types of Pulleys: fixed Pulleys and movable Pulleys. Fixed Pulleys are attached to a stationary object and do not move. They change the direction of the force but do not provide mechanical advantage. On the other hand, Movable Pulleys move along with the load being lifted, providing a mechanical advantage by reducing the force needed to lift the load.
Pulleys – Types and Applications have several Applications in the human system, including the movement of limbs, force amplification, joint stabilization, and weightlifting. Understanding the different Types and Applications of Pulleys is essential for understanding their role in the human body and designing effective exercise programs and medical interventions. Pulley systems are commonly used in various applications, such as elevators, cranes, and construction equipment. They are also used in everyday items such as window blinds, exercise equipment, and garage doors.
Read more: Read more about Centre Of Gravity Of The Human Body
Table of Contents
Pulleys in the Human System
In the human body, Pulleys are involved in the movement of muscles and tendons. These Pulleys, also known as tendon sheaths, help to guide and stabilize the tendons as they move through the body.
The Pulleys – Types and Applications in the human body are located in areas such as the fingers, wrists, and ankles. In these areas, the tendons pass through several Pulleys that keep them in place and prevent them from popping out of position.
For example, the fingers have several Pulleys along the path of the flexor tendons that allow us to bend and straighten our fingers. These Pulleys help to prevent the tendons from bowstringing (turning outward) as we move our fingers. If the Pulleys are damaged or inflamed, it can lead to a condition called trigger finger, where the finger becomes stuck in a bent position.
Similarly, the ankle joint has several Pulleys that guide the tendons of the foot and ankle muscles, allowing us to move our feet and toes. Injuries to these Pulleys can lead to conditions such as ankle impingement or tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Overall, Pulleys play an essential role in the movement and stability of the human body, and their proper function is necessary for regular bodily activity.
Types of Pulleys
Types of pulleys are as follow:
- Fixed Pulleys,
- Movable Pulleys
- Anatomic pulleys and
- Compound pulleys.
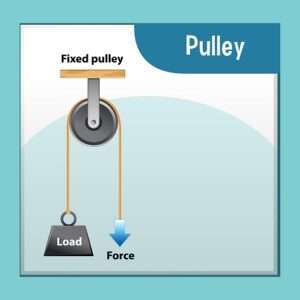
Fixed Pulleys:
Fixed Pulleys are stationary and do not move along with the tendon or muscle. They act as a stable anchor point for the tendon and help change the applied force’s direction. Fixed Pulleys are commonly found at the beginning and end of a muscle or tendon’s path, where they help to transmit the power generated by force to the bone.
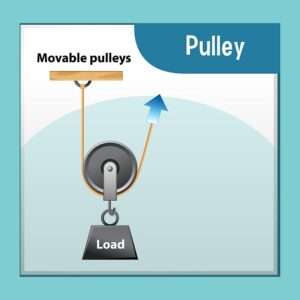
Movable Pulleys:
Movable Pulleys move along with the tendon or muscle and are attached to the bone via ligaments. They help to amplify the force generated by the power, making it easier to move a load. Movable Pulleys are commonly found in the middle of a muscle or tendon’s path, where they help to increase the mechanical advantage of the muscle.
Examples of movable Pulleys in the human system include the patella or kneecap, which acts as a pulley for the quadriceps muscle, and the Pulleys in the fingers and wrist that guide the flexor and extensor tendons.
Both fixed and movable Pulleys are essential in the human system, as they help to transmit force from muscles to bones, allowing us to move and perform a wide range of activities.
Anatomic Pulleys:
Anatomic Pulleys are a type of Pulleys – Types and Applications found in the human body. They are formed by fibrous tissue called retinacula, which hold tendons in place as they pass over bony prominences or around joints. These Pulleys help to maintain the proper alignment of tendons as they move through their range of motion, reducing friction and preventing excessive wear and tear.
The human body has several anatomic Pulleys, such as the Pulleys in the fingers, thumb, wrist, ankle, and foot. For example, the flexor retinaculum in the wrist forms a pulley system for the hand’s tendons, allowing for smooth and efficient movement of the fingers. In the foot, the plantar aponeurosis creates a pulley system for the tendons, helping to maintain the foot’s arch and providing support during walking and running.
Anatomic Pulleys part of Pulleys – Types and Applications are essential for the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system and can become damaged or disrupted due to injury or overuse. This can lead to conditions such as tendonitis or trigger finger, which can cause pain and limited mobility. Treatment for these conditions may include rest, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical repair of the damaged pulley system.
Compound Pulley
A compound pulley is a combination of fixed and moveable Pulleys. It offers direction change and force reduction, making it machine efficient. The compound pulley comprises multiple Pulleys mounted on a standard shaft or axle, with a single rope or cable passing through them all.
The moveable pulley is attached to the load in a compound pulley system, while the fixed Pulleys are connected to a support structure. As the limitation is lifted, the moveable pulley moves up, reducing the force required to lift the load. The direction of the force is also changed, allowing the load to be raised in a different order than the applied force.

Compound Pulleys are commonly used in cranes, where heavy loads must be lifted to great heights. Using a compound pulley system significantly reduces the force required to lift the load, making it easier and more efficient to lift heavy loads. Compound Pulleys are also used in weightlifting machines to provide resistance during exercise and in sailing to adjust the tension on the sails.
Compound Pulleys which are part of Pulleys – Types and Applications are handy machine that combines the benefits of fixed and moveable Pulleys to provide a significant mechanical advantage, making it easier to lift heavy loads and reduce the required force.
Examples of Fixed Pulley in the Human Body
Fixed Pulleys are stationary and act as a stable anchor point for the tendon or muscle. They change the direction of the applied force and are commonly found at the beginning and end of a muscle or tendon’s path, where they help to transmit the force generated by the muscle to the bone.
Examples Of Fixed Pulleys In The Human Body Include:
- Trochlea: The trochlea is a fixed pulley located in the elbow joint. It helps to change the direction of the force generated by the biceps and triceps muscles, allowing us to bend and straighten our arms.
- Acetabulum: The acetabulum is a fixed pulley located in the hip joint. It helps to transmit the force generated by the hip muscles to the femur bone, allowing us to move our legs and hips.
- Glenoid Cavity: The glenoid cavity is a fixed pulley located in the shoulder joint. It helps to transmit the force generated by the rotator cuff muscles to the humerus bone, allowing us to move our arms and shoulders.
- Patella: The patella, or kneecap, is a movable pulley in the knee joint. However, it also acts as a fixed pulley for the quadriceps muscle. It helps to change the direction of the force generated by the quadriceps muscle, allowing us to straighten our legs.
Overall, fixed Pulleys which are part of Pulleys – Types and Applications play an essential role in the human body by transmitting the force generated by muscles to the bones, allowing us to move and perform a wide range of activities.
Examples of Moveable Pulley in the Human Body
Movable Pulleys move along with the tendon or muscle and are attached to the bone via ligaments. They help to amplify the force generated by the muscle, making it easier to move a load. Movable Pulleys are commonly found in the middle of a muscle or tendon’s path, where they help to increase the mechanical advantage of the muscle.
Examples of Movable Pulleys
- Patella (Kneecap): The patella is a movable pulley in the knee joint. It is attached to the quadriceps tendon and helps increase the quadriceps muscle’s mechanical advantage. This makes it easier to extend the leg and straighten the knee.
- Flexor Retinaculum: The flexor retinaculum is a band of connective tissue in the wrist. It acts as a movable pulley for the flexor tendons of the hand, helping to increase the mechanical advantage of these muscles and making it easier to grip objects.
- Extensor Hood: The extensor hood is a fibrous structure at the top of the fingers. It acts as a movable pulley for the extensor tendons of the hand, helping to increase the mechanical advantage of these muscles and making it easier to extend the fingers.
- Calcaneal Tendon (Achilles Tendon): The calcaneal tendon, also known as the Achilles tendon, is a movable pulley in the ankle joint. It is attached to the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. It helps to increase the mechanical advantage of these muscles, making it easier to push off the ground and lift the heel during walking, running, and jumping.
Overall, movable Pulleys play an essential role in the human body by helping to amplify the force generated by muscles, making it easier to move and perform a wide range of activities.
Examples of Anatomic Pulleys in the Human Body
There are several anatomic Pulleys in the human body, formed by fibrous tissue called retinacula, which hold tendons in place as they pass over bony prominences or around joints. Here are some examples of anatomic Pulleys in the human body:
- Flexor Retinaculum: The flexor retinaculum is a band of connective tissue in the wrist. It acts as an anatomic pulley for the flexor tendons of the hand, helping to maintain their proper alignment and reducing friction as they pass through the carpal tunnel.
- Patellar Retinaculum: A patellar retinaculum is a group of fibrous bands that attach to the patella (kneecap) and help to stabilize the patellar tendon. They form an anatomic pulley system that allows the patellar tendon to move smoothly as the knee is bent and straightened.
- Pulleys of the Fingers: The fingers have several anatomic Pulleys that hold the flexor tendons in place as they pass over the bones of the hand. These Pulleys help to maintain the proper alignment of the tendons, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement of the fingers.
- Plantar Aponeurosis: Plantar aponeurosis is a thick band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, helping to maintain the arch of the foot and providing support during walking and running. It also forms an anatomic pulley system for the foot’s tendons, helping keep their proper alignment and reducing friction as they move.
Overall, anatomic Pulleys which are part of Pulleys – Types and Applications play an essential role in the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system, and disruption of these Pulleys can lead to conditions such as tendonitis or trigger finger.
Examples of Compound Pulleys in the Human Body
There are no examples of compound Pulleys in the human body, as the musculoskeletal system does not use multiple Pulleys mounted on a standard shaft or axle. However, the human body does use multiple anatomic Pulleys, which can work together to create a mechanical advantage similar to a compound pulley system.
For example, in the fingers, multiple anatomic Pulleys are formed by the retinaculum holding the tendons close to the bone. These Pulleys work together to create a mechanical advantage, allowing the finger to bend and straighten with less force required from the muscles.
Similarly, in the knee joint, there are anatomic Pulleys formed by the patellar tendon and the retinaculum that helps maintain the joint’s proper alignment and reduce friction as the knee moves. These anatomic Pulleys create a mechanical advantage, reducing the force required to bend and straighten the knee joint.
While these anatomic Pulleys are not technically compound, they work together to create a mechanical advantage similar to a compound pulley system, making movement in the body more efficient and reducing the force required to move the joints.
Applications of Pulleys in the Human System
Pulleys have several essential Applications in the human body, especially the musculoskeletal system. Here are some Applications of Pulleys in the human system:
- Movement of Limbs: The pulley systems formed by tendons and retinacula allow for efficient movement of the limbs, reducing friction and wear and tear on the muscles and joints. The fingers, wrist, ankle, and foot Pulleys are essential for fine motor control and precise movements.
- Force Amplification: Pulleys can also amplify the force generated by muscles. For example, the masseter muscle uses a pulley system in the jaw to increase the force generated during chewing, allowing for more efficient mastication.
- Joint Stabilization: Anatomic Pulleys help to stabilize joints by maintaining the proper alignment of tendons and reducing friction as they move. For example, the patellar retinaculum in the knee stabilizes the patellar tendon and reduces the risk of dislocation.
- Weightlifting: Pulleys are also used in weightlifting machines to provide resistance during exercise. The Pulleys can be adjusted to vary the amount of weight lifted and target specific muscle groups.
- Proper Functioning of the Musculoskeletal System: The human body has several anatomic Pulleys formed by tendons and retinacula that help to maintain the appropriate alignment of tendons and reduce friction as they move. Understanding these Pulleys is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system, ensuring efficient movement, and reducing wear and tear on the muscles and joints.
- Exercise and Rehabilitation: Pulleys are used in weightlifting machines to provide resistance during exercise. Understanding the different Types of Pulleys and their Applications is essential for designing effective exercise programs and rehabilitation protocols.
- Medical Interventions: Understanding Pulleys is also essential in medical interventions, such as surgeries or joint replacements. Surgeons may need to repair or reconstruct anatomic Pulleys to restore proper joint function, and knowledge of Pulleys is essential for designing and implementing these interventions.
- Engineering and Design: Pulleys are used in various machines and equipment, from cranes to elevators to bicycles. Understanding the different Types and Applications of Pulleys is necessary for designing and building efficient and effective devices.
In summary, understanding Pulleys are necessary for maintaining the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system, designing effective exercise programs and rehabilitation protocols, implementing medical interventions, and engineering and designing machines and equipment.
Overall, Pulleys – Types and Applications play an essential role in the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system, allowing for efficient movement, force amplification, joint stabilization, and exercise.
SUMMARY
Pulleys are simple machines with a grooved wheel and a rope or cable that passes over it. They have several Types and Applications in the human system.
Types of Pulleys:
Fixed Pulleys: The wheel is fixed in place and only changes the direction of the force.
Moveable Pulleys: The wheel is attached to the object being moved and reduces the force required to lift it.
Anatomic pulleys:
Compound Pulleys: A combination of fixed and moveable Pulleys offers direction change and force reduction.
Applications of Pulleys in the Human System:
Movement of limbs, providing efficient training, and reducing friction and wear and tear on the muscles and joints.
Force amplification, particularly in the jaw muscles, for more efficient chewing.
Joint stabilization by maintaining the proper alignment of tendons and reducing friction as they move.
Weightlifting, in which Pulleys are used in weightlifting machines to provide resistance during exercise.
In addition, there are anatomic Pulleys formed by tendons and retinacula in the human body, particularly in the fingers, wrist, ankle, and foot, which play a vital role in the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system.

5 Responses